CPU time Wikipedia. CPU Time on Single CPU Multi Tasking System. CPU color time for program P1. CPU time or process time is the amount of time for which a central processing unit CPU was used for processing instructions of a computer program or operating system, as opposed to, for example, waiting for inputoutput IO operations or entering low power idle mode. The CPU time is measured in clock ticks or seconds. Often, it is useful to measure CPU time as a percentage of the CPUs capacity, which is called the CPU usage. CPU time and CPU usage have two main uses. The first use is to quantify the overall busyness of the system. When the CPU usage is above 7. Such high CPU usage indicates insufficient processing power. Either the CPU needs to be upgraded, or the user experience reduced, for example, by switching to lower resolution graphics or reducing animations. The second use, with the advent of multi tasking, is to quantify how the processor is shared between computer programs. High CPU usage by a single program may indicate that it is highly demanding of processing power or that it may malfunction for example, it has entered an infinite loop. CPU time allows to measure how much processing power a single program requires, eliminating interference, such as time executed waiting for input or being suspended to allow other programs to run. In contrast, elapsed real time or simply real time, or wall clock time is the time taken from the start of a computer program until the end as measured by an ordinary clock. Elapsed real time includes IO time and all other types of waits incurred by the program. SubdivisioneditCPU time or CPU usage can be reported either for each thread, for each process or for the entire system. Moreover, depending on what exactly the CPU was doing, the reported values can be subdivided in User time is the amount of time the CPU was busy executing code in user space. System time is the amount of time the CPU was busy executing code in kernel space. If this value is reported for a thread or process, then it represents the amount of time the kernel was doing work on behalf of the executing context, for example, after a thread issued a system call. Idle time for the whole system only is the amount of time the CPU was not busy, or, otherwise, the amount of time it executed the System Idle process. Capture.jpg' alt='Priority Cpu Scheduling Program C' title='Priority Cpu Scheduling Program C' />Understanding CPU utilization Types of processes. Interactive processes interact constantly with their users, and therefore spend a lot of time waiting for keypresses. And finally, the Cisco Flow Processor uses a software architecture based on a full ANSIC development environment implemented in a true parallel processing environment. AutoSys is used for defining, scheduling and monitoring jobs. These jobs can be a UNIX script, java program or any other program which can be invoked from shell. This document discusses the configuration of upstream scheduler mode for the Cisco Universal Broadband Router uBR series of Cable Modem Termination Systems CMTS. This set of Operating System Multiple Choice Questions Answers MCQs focuses on CPU Scheduling. Which module gives control of the CPU to the process. MTJhWLpKM/WQv_YZg-dqI/AAAAAAAAAa8/kCOGiyTTTqERdYf7KX6GFg1GCVim4m-AACLcB/s1600/priority.JPG' alt='Priority Cpu Scheduling Program C' title='Priority Cpu Scheduling Program C' />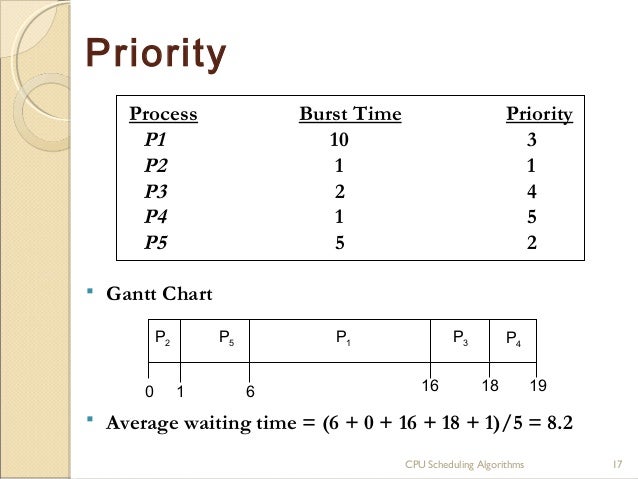
Admin. We are a group of young techies trying to provide the best study material for all Electronic and Computer science students. We are publishing Microcontroller. CPU time or process time is the amount of time for which a central processing unit CPU was used for processing instructions of a computer program or operating. Idle time actually measures unused CPU capacity. Steal time for the whole system only, on virtualized hardware, is the amount of time the operating system wanted to execute, but was not allowed to by the hypervisor. This can happen if the physical hardware runs multiple guest operating system and the hypervisor chose to allocate a CPU time slot to another one. Unix commands for CPU timeeditUnix command topeditThe Unix command top provides CPU time, priority, elapsed real time, and other information for all processes and updates it in real time. Unix command timeeditThe Unix command time prints CPU time and elapsed real time for a Unix process. Prime. Number. c o next. Prime. Number. time. Prime. Number 3. 00. Priority Cpu Scheduling Program C' title='Priority Cpu Scheduling Program C' />Prime number greater than 3. Ssl Setup Apache Windows Install. This process took a total of 0. CPU time, out of which 0. Elapsed real time was 1. The following is the source code of the application next. Prime. Number which was used in the above example. Prime. Number. cincludelt stdio. Prime. Numberunsignedlongintnforinti2 ilt n 1 iifni0return. NULL,1. 0,nargument while Prime. Numbern printfPrime number greater than lu is lun,argument,n return. POSIX functions clock and getrusageeditPOSIX functionsclock and getrusage can be used to get CPU time consumed by any process in a POSIX environment. If the process is multithreaded, the CPU time is the sum for all threads. With Linux starting from kernel 2. RUSAGETHREAD which leads to resource usage statistics for the calling thread only. Total CPU timeeditOn multi processor machines, a computer program can use two or more CPUs for processing using parallel processing scheduling. In such situations, the notion of total CPU time is used, which is the sum of CPU time consumed by all of the CPUs utilized by the computer program. CPU time and elapsed real timeeditElapsed real time is always greater than or equal to the CPU time for computer programs which use only one CPU for processing. If no wait is involved for IO or other resources, elapsed real time and CPU time are very similar. CPU time and elapsed real time for parallel processing technologyeditIf a program uses parallel processing, total CPU time for that program would be more than its elapsed real time. Total CPU timeNumber of CPUs would be same as elapsed real time if the work load is evenly distributed on each CPU and no wait is involved for IO or other resources. Example A software application executed on a Hexa core processor creates three Unix processes for fulfilling the user requirement. Each of these three processes creates two threads, enumerating a total of 6 working threads. Computation is distributed evenly on the 6 independent threads. If no wait for resources is involved, total CPU time is expected to be six times the elapsed real time. See alsoeditReferenceseditExternal linkseditThimmannagari, Chandra 2. CPU Design Answers to Frequently Asked Questions. Springer. p. 6. 8.